Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2018, Vol. 22 ›› Issue (36): 5872-5878.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.0397
Previous Articles Next Articles
Biological mechanism of oxidative stress induced by mechanical stimulation in the development of diseases
Shi Peipei, Li Xiaona, Wei Junchao, Song Jie
- (Institute of Mechanics, Taiyuan University of Technology, Taiyuan 030024, Shanxi Province, China)
-
Received:2018-04-25Online:2018-12-28Published:2018-12-28 -
Contact:Li Xiaona, PhD, Associate professor, Master’s supervisor, Institute of Mechanics, Taiyuan University of Technology, Taiyuan 030024, Shanxi Province, China -
About author:Shi Peipei, Master candidate, Institute of Mechanics, Taiyuan University of Technology, Taiyuan 030024, Shanxi Province, China -
Supported by:the National Natural Science Foundation of China, No. 11572213 and 11402162; the International Cooperation and Exchange Program of Shanxi Province, No. 201703D421019
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Shi Peipei, Li Xiaona, Wei Junchao, Song Jie. Biological mechanism of oxidative stress induced by mechanical stimulation in the development of diseases [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2018, 22(36): 5872-5878.
share this article
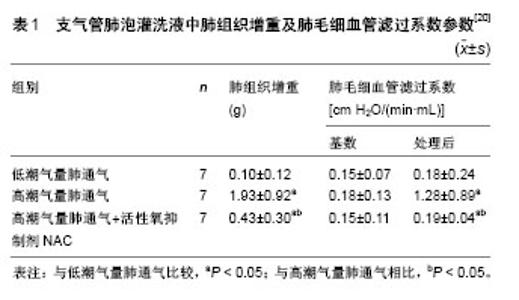
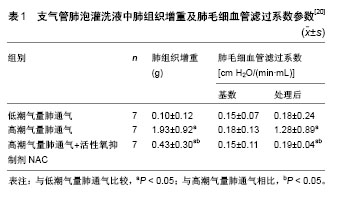
2.1 力学刺激介导的氧化应激对肺组织损伤的影响 呼吸机通过机械通气控制或改变机体的自主呼吸运动,被广泛应用于临床上急性肺损伤和急性呼吸窘迫综合征的治疗[13]。但不适当的机械通气可损害血气屏障,增加肺组织通透性,加剧肺损伤,造成呼吸机相关性肺损伤[14],其主要特征是肺泡细胞功能紊乱和肺部炎症,进而表现出肺部水肿和急性呼吸衰竭[15]。目前机械通气介导的呼吸机相关性肺损伤发病机制尚不清楚,可能与异常力学刺激诱导的活性氧异常累积有关[16]。 为研究肺损伤的致病机制,体外实验大多以不同幅度的周期性机械牵拉处理体外培养的肺组织细胞,模拟生理性呼吸或以呼吸机为载体的人工机械通气;体内实验大多采用动物的离体肺-再灌注模型,以自主性呼吸或低潮气量机械通气为对照,对实验动物进行高潮气量机械通气诱导肺损伤[17,19-21]。无论是体外或是体内的异常力学因素,均可使肺组织细胞氧化及抗氧化产物失衡,处于较高氧化应激状态,并通过一系列信号级联反应诱导细胞凋亡、炎性细胞浸润、细胞间连接蛋白结构改变、细胞通透性增加等,成为呼吸机相关性肺损伤的重要致病因子。体外实验表明,高幅度周期性牵拉(幅度15%以上)可使人呼吸道上皮细胞系16HBE、肺泡Ⅱ型细胞系 A549 及大鼠Ⅱ型肺泡细胞过氧化物离子(O2-)的表达显著上调,参与呼吸机相关性肺损伤的早期发生和发展[16],表明肺组织的过度牵张可能通过肺上皮细胞活性氧的产生造成肺组织损伤。对大鼠Ⅰ型或Ⅱ型肺泡上皮细胞进行高幅度周期性牵拉,可显著增加活性氧、超氧化物、一氧化氮及细胞色素C的水平,降低细胞线粒体膜电位;对实验大鼠进行高潮气量(25 mL/kg)肺通气,也可检测到其肺组织或肺灌注液中活性氧等氧化产物水平的增加[17]。氧化产物的增加可通过细胞外调节 蛋白激酶ERK及NF-κB等信号通路,使肺泡上皮细胞处于较高氧化应激状态,造成细胞或组织通透性增加及细胞凋亡,外源性过氧化物及一氧化氮刺激也可造成未受牵拉的上皮细胞通透性增加[17-18]。信号通路 NF-κB 抑制剂MG132,过氧化物清除剂钛试剂Tiron或mito-Tempo可有效缓解牵拉诱导的细胞或组织通透性增加[17];活性氧抑制剂维生素E及细胞色素C抑制剂环孢霉素A可显著降低牵拉引起的细胞凋亡[18]。体外及体内实验均表明,抗氧化剂在细胞或组织损伤中具有显著的保护效应,可能在呼吸机相关性肺损伤中起到预防和治疗作用。 异常力学因素所介导的多种氧化产物的过量累积,也可促进炎性或前炎性细胞因子释放,参与呼吸机相关性肺损伤的发生发展。对小鼠肺泡巨噬细胞的体外周期性牵拉或对实验小鼠的高潮气量(28 mL/kg)体内机械通气,均可通过线粒体活性氧的过度产生激活NOD样受体蛋白3(NLRP3)炎症小体,并通过半胱天冬酶1和Toll样受体4诱导白细胞介素1β、白细胞介素18 释放,加剧力学刺激诱导的肺部炎症及肺损伤,其中NLRP3炎症小体可能是呼吸机相关性肺损伤的潜在治疗靶点[19]。其他动物实验也证明了高潮气量(15 mL/kg)机械通气可使肺组织及肺灌注液中产生过量的活性氧,并通过NF-κB、半胱天冬酶3激活MAPK的一系列级联反应及促炎性细胞因子(如白细胞介素1β、肿瘤坏死因子α)响应,最终导致肺组织通透性增加、细胞凋亡等急性肺损伤。线粒体活性氧抑制剂NAC可显著降低相关细胞因子的释放,对急性肺损伤起到一定的保护作用,表现为肺组织增重及肺毛细血管滤过系数显著降低,如表1所示[20]。"
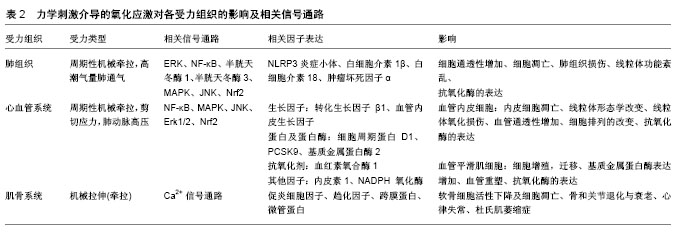
另外,高潮气量肺通气还可通过活性氧的产生造成线粒体功能紊乱,造成肺内皮屏障性功能障碍。天然抗氧化剂白藜芦醇可通过Nrf2介导的信号通路启动细胞防御,Nrf2通过向核内转移并与下游抗氧化反应原件ARE相结合,启动一系列抗氧化酶的表达,抑制线粒体的氧化损伤,Nrf2的敲除会导致天然抗氧化剂失去其保护效应[21]。 临床上对急性呼吸衰竭患者进行呼吸机治疗前,会给予患者高氧抢救,长时间暴露于高氧环境或高潮气量机械通气都能引起肺损伤。有研究者对实验小鼠高氧预处理12 h后再进行高潮气量肺通气与高氧联合作用,证实该模型同样会诱导肺组织产生过量活性氧,通过激活MAPK家族的JNK及下游促凋亡信号半胱天冬酶3、PARP-1造成肺组织损伤,且损伤程度高于单独的高氧刺激或力刺激。对小鼠肺上皮细胞MLE-12周期性牵拉的同时给予高氧环境联合作用,同样会由于活性氧的过量产生诱导肺上皮细胞凋亡。活性氧抑制剂NAC可通过抑制JNK的活化,有效缓解细胞凋亡和肺损伤[22]。 2.2 力学刺激介导的氧化应激对心血管疾病的影响 正常生理状态下,血管壁处于不断流动的血液中,主要受到剪切应力、周向拉应力和静水压力[23],是内皮稳态的必要条件。异常的拉应力或切应力等血流动力学的变化,能够破坏血管稳态[24],影响血管结构调节、血管肌源性收缩和血管活性物质的功能性反应等[25],表现出内皮功能障碍、血管炎症和血管重建[26],与慢性高血压、动脉粥样硬化和冠心病等多种心血管疾病密切相关[27-29]。目前血流动力学的变化与心血管疾病之间的关系仍在进一步研究中,其中异常的力学刺激可诱导活性氧等过氧化产物的增加,并通过氧化还原相关信号通路的活化对相关疾病发生发展起到重要调控作用。 体外周向拉应力可改变血管内皮细胞的氧化及抗氧化产物平衡,使血管稳态失衡,参与心血管疾病的发生发展。生理水平的周期性牵拉(拉伸幅度6%,频率 1 Hz),可通过活性氧-Nrf2 信号通路激活抗氧化剂血红素氧合酶1的活性,抑制人主动脉内皮细胞HAECs炎性因子介导的内皮细胞凋亡,维持血管稳态,这种保护作用能够被血红素氧合酶1的抑制剂所逆转[30]。对人脐静脉内皮细胞(HUVECs)进行生理水平的周期性机械牵拉,也可显著增加活性氧的水平及NADPH氧化酶活性。氧化产物的增加伴随着NF-κB信号通路活性的增强,且NADPH氧化酶抑制剂可通过抑制NF-κB信号通路活性显著降低活性氧水平,表明NADPH氧化酶可能是活性氧的主要来源。高幅度周期性牵拉(20%),不仅能增加人脐静脉内皮细胞内的活性氧及NADPH氧化酶水平,也能显著影响血管收缩剂内皮素1的活性,成为动脉粥样硬化病变的潜在起始信号[31-32]。另外,体外超生理水平(20%,1 Hz,1 h)周期性牵拉,可引起小牛主动脉内皮细胞BAECs朝着牵拉方向垂直排列,线粒体明显缩短,且线粒体形态的变化与细胞排列密切相关[33]。对小鼠肺血管内皮细胞进行体外高幅度(20%)周期性牵拉或对实验小鼠进行高潮气量肺通气,也可通过活性氧的过度产生引发线粒体氧化损伤及功能紊乱,造成肺血管内皮屏障性功能障碍[21]。白藜芦醇和抗氧化剂 NAC可通过Nrf2 介导的信号通路激活抗氧化酶的表达,抑制线粒体的氧化损伤,还可通过干扰 ERK信号通路、抑制NADPH氧化酶的表达降低活性氧水平,这些分子生物学机制可为异常力学刺激诱导的心血管疾病提供新的治疗靶点,起到重要调控作用[21,31-32]。 由于血流动力学改变所产生的异常剪切应力,同样与心血管疾病相关。体外施加脉动式生理性 (0.15 mN/cm2)或病理性(0.3 mN/cm2)剪切应力可增加人血管内皮细胞系CRL1730中活性氧水平,改变线粒体形态,使之产生功能障碍,而持续性高剪切力对其则没有显著影响,说明模拟体内环境的脉动式剪切应力在体外实验中的可行性及必要性[34]。低剪切力 (0.03-0.06 mN/cm2)刺激下人血管内皮细胞及血管平滑肌细胞中活性氧的增加,可促进前蛋白转化酶枯草溶菌素9(proprotein convertase subtilisin/kexin type 9,PCSK9)过高表达,采用小鼠动物模型同样观察到具有较低剪切力的主动脉分支及主动脉-髂动脉分支处 PCSK9表达水平较高,且活性氧与PCSK9间存在明显的正反馈作用。采用活性氧抑制剂二亚苯基烟碱氯化物 DPI或夹竹桃麻素可降低PCSK9的表达,敲除PCSK9相关基因也可抑制活性氧的表达,这样的相互作用机制可能与低剪切力作用下动脉粥样硬化的形成有关[35]。 血管平滑肌细胞的增殖、收缩、合成细胞外基质等各种生理功能的行使,也依赖于力学刺激诱导的活性氧的生成。肺血流量增加产生的肺动脉高压,可引起小羊肺血管平滑肌细胞转化生长因子β1和血管内皮生长因子表达增加[36]。且体外周期性牵拉可通过激活转化生长因子β1介导的NADPH氧化酶及活性氧的产生,促使肺血管平滑肌细胞中血管内皮生长因子表达上调并参与血管重塑[37]。小羊动脉导管产前结扎诱导的新生儿持续性肺动脉高压模型,也可通过线粒体复合物Ⅲ介导NF-κB信号通路活化,导致肺血管平滑肌细胞4型NADPH氧化酶、活性氧及细胞周期蛋白D1的过高表 达[38],这些分子的靶向治疗可降低与新生儿持续性肺动脉高压相关的血管重构。对新生大鼠肺血管平滑肌细胞超生理水平(20%)的周期性牵拉,可显著增加细胞培养液中活性氧、过氧化氢、过氧化亚硝酸盐、一氧化氮合酶1、4型NADPH氧化酶等的表达[39],活性氧的产生还可激活p38、JNK和Erk1/2在内的MAPK信号通路[40],最终导致肺血管重塑及肺动脉高压。超氧化物清除剂、非特异性 NADPH氧化酶或一氧化氮合酶抑制剂、过氧化亚硝酸分解催化剂及小干扰 RNA介导的一氧化氮合酶1或4型NADPH氧化酶的敲除,均能降低高幅度周期性牵拉诱导的氧化产物的增加。血管重塑包括平滑肌肥厚、增生、胶原蛋白的分解和细胞外基质重组等,这一过程涉及基质金属蛋白酶的表达及其酶活性,它可分解原有的细胞外基质支架,同时合成新的细胞外基质进行血管重构。高幅度机械牵拉可通过 NADPH氧化酶诱导活性氧的产生,促使 C57BL/6小鼠血管平滑肌细胞中基质金属蛋白酶2的表达,导致血管重塑[41]。基质金属蛋白酶还可通过降解细胞外基质而削弱血管壁的力学强度,在动脉粥样硬化病变中发挥重要作用[42]。 2.3 力学刺激介导的氧化应激对其他组织相关疾病的影响 在肌骨系统中,骨关节炎是一种常见的退行性关节疾病,与衰老及不良的生活方式,如肥胖和过度使用关节等密切相关[43]。作用于关节软骨的机械力可诱导软骨细胞产生过量的活性氧,直接损害软骨细胞DNA,诱导细胞产生促炎细胞因子和趋化因子,导致软骨细胞活性下降及细胞凋亡,加速骨和关节退化与衰老的过程[44]。在横纹肌中,机械拉伸可通过跨膜蛋白NADPH氧化酶2激活活性氧和活性氮的表达,影响Ca2+信号通路和肌肉收缩功能。机械牵拉亦可通过微管蛋白激活心肌和骨骼肌细胞产生过度的活性氧,导致Ca2+依赖性心律失常或杜氏肌萎缩症等疾病[45]。当角膜长期受到机械性损伤(揉眼、佩戴隐形眼镜),加之眼内压的作用,处于复杂的应力环境中,极易造成氧化损伤,导致角膜内皮营养不良和圆锥角膜等疾病的产生[46]。研究表明,体外培养的圆锥角膜细胞具有较高的氧化应激水平,且其抗氧化系统的活化存在一定缺陷[47-49]。角膜扩张性疾病还可导致角膜力学环境发生改变,诱导炎性因子、基质降解酶等的产生。力学刺激介导的氧化应激对各受力组织的影响及其相关信号通路、细胞因子表达,如表2所示。"
| [1] Lobo V,Patil A,Phatak A,et al.Free radicals, antioxidants and functional foods: impact on human health.Pharmacogn Rev.2010;4(8):118-126.[2] Uhl L,Gerstel A,Chabalier M,et al.Hydrogen peroxide induced cell death: one or two modes of action.Heliyon.2015;1(4):e00049.[3] Rahman K.Studies on free radicals, antioxidants, and co-factors.Clin Interv Aging.2007; 2(2): 219-236.[4] Morita M,Naito Y,Yoshikawa T,et al.Plasma lipid oxidation induced by peroxynitrite, hypochlorite, lipoxygenase and peroxyl radicals and its inhibition by antioxidants as assessed by diphenyl-1-pyrenylphosphine. Redox Biol.2016;8:127-135.[5] Aslani BA,Ghobadi S.Studies on oxidants and antioxidants with a brief glance at their relevance to the immune system.Life Sci. 2016;146: 163-173.[6] Ranchoux B,Meloche J,Paulin R,et al.DNA damage and pulmonary hypertension.Int J Mol Sci.2016;17(6):990.[7] Niedzielska E,Smaga I,Gawlik M,et al.Oxidative Stress in Neurodegenerative Diseases.Mol Neurobiol.2016;53(6):4094-4125.[8] Hofer T,Perry G.Nucleic acid oxidative damage in Alzheimer’s disease-explained by the hepcidin-ferroportin neuronal iron overload hypothesis?J Trace Elem Med Biol.2016;38:1-9.[9] Bonomini F,Rodella LF,Rezzani R.Metabolic syndrome, aging and involvement of oxidative stress.Aging Dis.2015;6(2):109-120.[10] Salvayre R,Negre-Salvayre A,Camaré C.Oxidative theory of atherosclerosis and antioxidants.Biochimie. 2016;125:281-296.[11] Prasad S,Gupta SC,Pandey MK,et al.Oxidative stress and cancer: advances and challenges. Oxid Med Cell Longev.2016;2016:1.[12] Wang JH,Li B.Mechanics rules cell biology.Sports Med Arthrosc Rehabil Ther Technol.2010; 2(16):1-7.[13] Del SL,Slutsky AS.Acute respiratory distress syndrome and multiple organ failure.Curr Opin Crit Care.2011;17(1):1-6.[14] Tian YFg,Gawlak G,O'Donnell JJ,et al.Modulation of Endothelial Inflammation by Low and High Magnitude Cyclic Stretch.PloS One. 2016;11(4):1-13.[15] Xia J,Li R,Yang R,et al.Mild hypothermia attenuate kidney injury in canines with oleic acid-induced acute respiratory distress syndrome. Injury.2016;47(7):1445-1451.[16] Chapman KE,Sinclair SE,Zhuang D,et al.Cyclic mechanical strain increases reactive oxygen species production in pulmonary epithelial cells.Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol.2005;289: L834-L841.[17] Davidovich N,DiPaolo BC,Lawrence GG,et al.Cyclic Stretch-Induced Oxidative Stress Increases Pulmonary Alveolar Epithelial Permeability. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol.2013;49(1):156-164.[18] Kuhn H,Nieuwenhuijsen H,Karthe B,et al.Stretch-induced apoptosis in rat alveolar epithelial cells is mediated by the intrinsic mitochondrial pathway.Exp Lung Res.2017;43(1):49-56.[19] Wu J,Yan Z,Schwartz DE,et al.Activation of NLRP3 inflammasome in alveolar macrophages contributes to mechanical stretch-induced lung inflammation and injury.J Immunol.2013;190(7): 3590-3599.[20] Chiang CH,Chuang CH,Liu SL,et al.N-acetylcysteine attenuates ventilator-induced lung injury in an isolated and perfused rat lung model.Injury.2012;43:1257-1263.[21] Dong WW,Liu YJ,Lv Z,et al.Lung endothelial barrier protection by resveratrol involves inhibition of HMGB1 release and HMGB1-induced mitochondrial oxidative damage via an Nrf2-dependent mechanism.Free Radic Biol Med.2015;88(Pt B):404-416. [22] Makena PS,Gorantla VK,Ghosh MC,et al.Lung injury caused by high tidal volume mechanical ventilation and hyperoxia is dependent on oxidant-mediated c-Jun NH2-terminal kinase activation.J Appl Physiol. 2011;111:1467-1476.[23] Hsieh HJ,Liu CA,Huang B,et al.Shear-induced endothelial mechanotransduction: the interplay between reactive oxygen species (ROS) and nitric oxide (NO) and the pathophysiological implications.J Biomed Sci.2014;21(3):1-15.[24] Matlung HL,Bakker EN,Van Bavel E.Shear stress, reactive oxygen species, and arterial structure and function.Antioxid Redox Signal. 2009;11(7):1699-1709.[25] Birukov KG.Cyclic Stretch, reactive oxygen species, and vascular remodeling.Antioxid Redox Signal.2009;11(7):1651-1667.[26] Montezano AC,Cat AND,Rios FJ,et al.Angiotensin II and vascular injury.Curr Hypertens Rep.2014;16(6):431. [27] Bentzon JF,Otsuka F,Virmani R,et al.Mechanisms of plaque formation and rupture.Circ Res. 2014;114(12):1852-1866.[28] Millon A,Sigovan M,Boussel L,et al.Low WSS Induces Intimal Thickening, while Large WSS Variation and Inflammation Induce Medial Thinning, in an Animal Model of Atherosclerosis.PLoS One. 2015;10(11):e0141880.[29] Gopal DM,Santhanakrishnan R,Wang YC,et al.Impaired right ventricular hemodynamics indicate preclinical pulmonary hypertension in patients with metabolic syndrome.J Am Heart Assoc.2015; 4:e001597.[30] Liu X,Peyton KJ,Durante W.Physiological cyclic strain promotes endothelial cell survival via the induction of heme oxygenase-1. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol.2013;304(12):H1634-H1643.[31] Liu JC,Chen JJ,Chan P,et al.Inhibition of cyclic strain-induced endothelin-1 gene expression by resveratrol.Hypertension. 2003;42: 1198-1205.[32] Matsushita H,Lee K,Tsao PS.Cyclic strain induces reactive oxygen species production via an endothelial NAD(P)H oxidase.J Cell Biochem Suppl.2001;36:99-106.[33] Shinmura A,Tsukamoto A,Hamada T,et al.Morphological dynamics of mitochondria in bovine aortic endothelial cell under cyclic stretch.Adv Biomed Eng.2015;4:60-66.[34] Chin LK,Yu JQ,Fu Y,et al.Production of reactive oxygen species in endothelial cells under different pulsatile shear stresses and glucose concentrations.Lab Chip.2011;11(11):1856-1863.[35] Ding Z,Liu S,Wang Xi,et al.Hemodynamic shear stress via ROS modulates PCSK9 expression in human vascular endothelial and smooth muscle cells and along the mouse aorta.Antioxid Redox Signal. 2015;22(9):760-771.[36] Mata-Greenwood E,Meyrick B,Soifer SJ,et al.Expression of VEGF and its receptors Flt-1 and Flk-1/KDR is altered in lambs with increased pulmonary blood flow and pulmonary hypertension.Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol.2003;285(1):L222-L231.[37] Mata-Greenwood E,Grobe A,Kumar S,et al.Cyclic stretch increases VEGF expression in pulmonary arterial smooth muscle cells via TGF-β1 and reactive oxygen species: a requirement for NAD(P)H oxidase.Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol.2005;289(2):L288-L298.[38] Wedgwood S,Lakshminrusimha S,Schumacker PT,et al.Cyclic stretch stimulates mitochondrial reactive oxygen species and Nox4 signaling in pulmonary artery smooth muscle cells.Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol.2015;309:L196-L203.[39] Dick AS,Ivanovska J,Kantores C,et al.Cyclic stretch stimulates nitric oxide synthase-1-dependent peroxynitrite formation by neonatal rat pulmonary artery smooth muscle. Free Radic Biol Med.2013;61: 310-319.[40] Chen Q,Li W,Quan Z,et al.Modulation of vascular smooth muscle cell alignment by cyclic strain is dependent on reactive oxygen species and P38 mitogen-activated protein kinase.J Vasc Surg. 2003;37(3): 660-668.[41] Grote K,Flach I,Luchtefeld M,et al.Mechanical stretch enhances mRNA expression and proenzyme release of matrix metalloproteinase-2 (MMP-2) via NAD(P)H oxidase-derived reactive oxygen species.Circ Res.2003;92:e80-e86.[42] Ellulu MS,Patimah I,Khaza'ai H,et al.Atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease: a review of initiators and protective factors. Inflammopharmacology.2016;24(1):1-10.[43] Greene MA,Loeser RF.Aging-related inflammation in osteoarthritis.Osteoarthritis Cartilage. 2015;23(11):1966-1971.[44] Yui N,Yudoh K,Fujiya H,et al.Mechanical and oxidative stress in osteoarthritis.J Phys Fit Sports Med.2016;5(1):81-86.[45] Ward CW,Prosser BL,Lederer WJ.Mechanical stretch-induced activation of ROS/RNS signaling in striated muscle.Antioxid Redox Signal.2014;20(6):929-936. [46] Liu X,Zhou D,Xie T,et al.Nrf2, a potential therapeutic target against oxidative stress in corneal diseases.Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2017; 2017:1-9.[47] Arnal E,Peris-Martínez C,Menezo JL,et al.Oxidative Stress in Keratoconus?Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci.2011;52(12):8592-8597.[48] Kiliç R,Cumurcu T,Sancaktar E,et al.Systemic Prolidase Activity and Oxidative Stress in Keratoconus.Curr Eye Res.2016;41(1):28-33.[49] Cantemir A,Alexa AI,Ciobica A,et al.Evaluation of atioxidant enzymes in keratoconus. Revista de Chimie.2016;67(8):1538-1541.[50] Kovac S,Angelova PR,Holmström KM,et al.Nrf2 regulates ROS production by mitochondria and NADPH oxidase.Biochim Biophys Acta.2015;1850(4):794-801.[51] Rodiño-Janeiro BK,Paradela-Dobarro B,Raposeiras-Roubín S,et al.Glycated human serum albumin induces NF-κB activation and endothelial nitric oxide synthase uncoupling in human umbilical vein endothelial cells.J Diabetes Complications.2015;29(8): 984-992.[52] Xiong S,Wang P, Ma L,et al.Ameliorating Endothelial Mitochondrial Dysfunction Restores Coronary Function via Transient Receptor Potential Vanilloid 1-Mediated Protein Kinase A/Uncoupling Protein 2 Pathway.Hypertension.2016;67(2):451-460.[53] Battelli MG,Polito L,Bortolotti M,et al.Xanthine Oxidoreductase-Derived Reactive Species: Physiological and Pathological Effects.Oxid Med Cell Longev.2016;2016:3527579.[54] Schramm A,Matusik P,Osmenda G,et al.Targeting NADPH oxidases in vascular pharmacology. Vasc Pharmacol.2012;56(5-6):216-231.[55] Marin T,Gongol B,Chen Z,et al.Mechanosensitive microRNAs-Role in endothelial responses to shear stress and redox state.Free Radic Biol Med.2013;64(6):61-68.[56] Amanso AM,Griendling KK.Differential roles of NADPH oxidases in vascular physiology and pathophysiology.Front Biosci (Landmark Ed). 2012;4(1):1044-1064.[57] Frey RS,Gao X,Javaid K,et al.Phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase gamma signaling through protein kinase Czeta induces NADPH oxidase-mediated oxidant generation and NF-kappaB activation in endothelial cells.J Biol Chem.2006;281(23):16128-16138.[58] Tkachev VO,Menshchikova EB,Zenkov NK.Mechanism of the Nrf2/Keap1/ARE signaling system.Biochemistry. 2011;76(4):407-422.[59] Cho HY,Kleeberger SR.Association of Nrf2 with airway pathogenesis: lessons learned from genetic mouse models.Arch Toxicol. 2015;89(11): 1931-1957. [60] Klaassen CD,Reisman SA.Nrf2 the rescue: effects of the antioxidative/electrophilic response on the liver.Toxicol Appl Pharmacol. 2010;244(1):57-65.[61] Ashino T,Yamamoto M,Numazawa S.Nrf2/Keap1 system regulates vascular smooth muscle cell apoptosis for vascular homeostasis: role in neointimal formation after vascular injury.Sci Rep. 2016;6(26291): 1-12. |
| [1] | Pu Rui, Chen Ziyang, Yuan Lingyan. Characteristics and effects of exosomes from different cell sources in cardioprotection [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(在线): 1-. |
| [2] | Zhang Tongtong, Wang Zhonghua, Wen Jie, Song Yuxin, Liu Lin. Application of three-dimensional printing model in surgical resection and reconstruction of cervical tumor [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1335-1339. |
| [3] | Pei Lili, Sun Guicai, Wang Di. Salvianolic acid B inhibits oxidative damage of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells and promotes differentiation into cardiomyocytes [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1032-1036. |
| [4] | Zeng Yanhua, Hao Yanlei. In vitro culture and purification of Schwann cells: a systematic review [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1135-1141. |
| [5] | Jiang Xin, Qiao Liangwei, Sun Dong, Li Ming, Fang Jun, Qu Qingshan. Expression of long chain non-coding RNA PGM5-AS1 in serum of renal transplant patients and its regulation of human glomerular endothelial cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(5): 741-745. |
| [6] | Xu Dongzi, Zhang Ting, Ouyang Zhaolian. The global competitive situation of cardiac tissue engineering based on patent analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(5): 807-812. |
| [7] | Wu Zijian, Hu Zhaoduan, Xie Youqiong, Wang Feng, Li Jia, Li Bocun, Cai Guowei, Peng Rui. Three-dimensional printing technology and bone tissue engineering research: literature metrology and visual analysis of research hotspots [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(4): 564-569. |
| [8] | Chang Wenliao, Zhao Jie, Sun Xiaoliang, Wang Kun, Wu Guofeng, Zhou Jian, Li Shuxiang, Sun Han. Material selection, theoretical design and biomimetic function of artificial periosteum [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(4): 600-606. |
| [9] | Liu Fei, Cui Yutao, Liu He. Advantages and problems of local antibiotic delivery system in the treatment of osteomyelitis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(4): 614-620. |
| [10] | Li Xiaozhuang, Duan Hao, Wang Weizhou, Tang Zhihong, Wang Yanghao, He Fei. Application of bone tissue engineering materials in the treatment of bone defect diseases in vivo [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(4): 626-631. |
| [11] | Zhang Zhenkun, Li Zhe, Li Ya, Wang Yingying, Wang Yaping, Zhou Xinkui, Ma Shanshan, Guan Fangxia. Application of alginate based hydrogels/dressings in wound healing: sustained, dynamic and sequential release [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(4): 638-643. |
| [12] | Chen Jiana, Qiu Yanling, Nie Minhai, Liu Xuqian. Tissue engineering scaffolds in repairing oral and maxillofacial soft tissue defects [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(4): 644-650. |
| [13] | Xing Hao, Zhang Yonghong, Wang Dong. Advantages and disadvantages of repairing large-segment bone defect [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(3): 426-430. |
| [14] | Jiang Tao, Ma Lei, Li Zhiqiang, Shou Xi, Duan Mingjun, Wu Shuo, Ma Chuang, Wei Qin. Platelet-derived growth factor BB induces bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells to differentiate into vascular endothelial cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(25): 3937-3942. |
| [15] | Luo Anyu, Liu Hanlin, Xie Xiaofei, Huang Chen. Effect of antioxidant mixture on structural degeneration of an osteoarthritis rat model [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(23): 3625-3629. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||